- I. Introduction
- II. Understanding Your Electric Vehicle
- III. Level 1 Charging: Home Outlets
- IV. Level 2 Charging: Dedicated EV Charging Stations
- V. Public Charging Options
- VI. Solar-Powered Charging
- VII. Energy Storage Systems
- VIII. Smart Charging Technologies
- IX. Government Incentives and Rebates
- X. Maintenance and Troubleshooting
- XI. Summary and Final Thoughts
- FAQs
- Conclusion
- Reading resources
- Blog series for EV charging
5 Takeaway Points regarding Electric vehicle charging:
- Home Charging Convenience: Level 1 charging at home provides cost-effective and convenient EV charging.
- Fast Charging Solutions: Dedicated Level 2 charging stations offer quicker replenishment for longer commutes.
- Exploring Public Charging: Learn about public charging networks and when to opt for them economically.
- Eco-Friendly Charging: Consider solar-powered solutions to reduce costs and environmental impact.
- Government Support: Discover incentives and rebates to make EV charging even more budget-friendly.

I. Introduction
Charging Electric Vehicles on a Budget: A Sustainable Solution
In today’s world, the push towards sustainability and eco-friendliness has never been more important. As we look for ways to reduce our carbon footprint, one area that demands attention is transportation. Electric vehicles (EVs) have emerged as a greener alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars and bikes, offering a cleaner and more sustainable mode of transportation. However, the concern of charging expenses can sometimes deter potential EV owners.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to share! website average bounce rate Buy traffic for your website
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the significance of charging electric vehicles on a budget. We’ll delve into various methods and technologies that allow you to keep your EV or electric bike charged without breaking the bank. From home charging solutions to solar-powered options and government incentives, this article will equip you with the knowledge needed to make eco-conscious and cost-effective choices.
II. Understanding Your Electric Vehicle
Getting to Know Electric Vehicles
Before we embark on our journey to discover budget-friendly charging options, let’s start by understanding electric vehicles themselves. EVs come in various forms, including electric cars, bikes, and scooters. Each type has its unique features and applications, but they all share a common goal: reducing emissions and promoting sustainability.
Battery Basics
At the heart of every electric vehicle lies its battery. Understanding battery types and their characteristics is crucial for optimizing your EV’s performance. Batteries can vary in chemistry, capacity, and charging capabilities, which can impact factors like range and charging speed.
Charging Methods
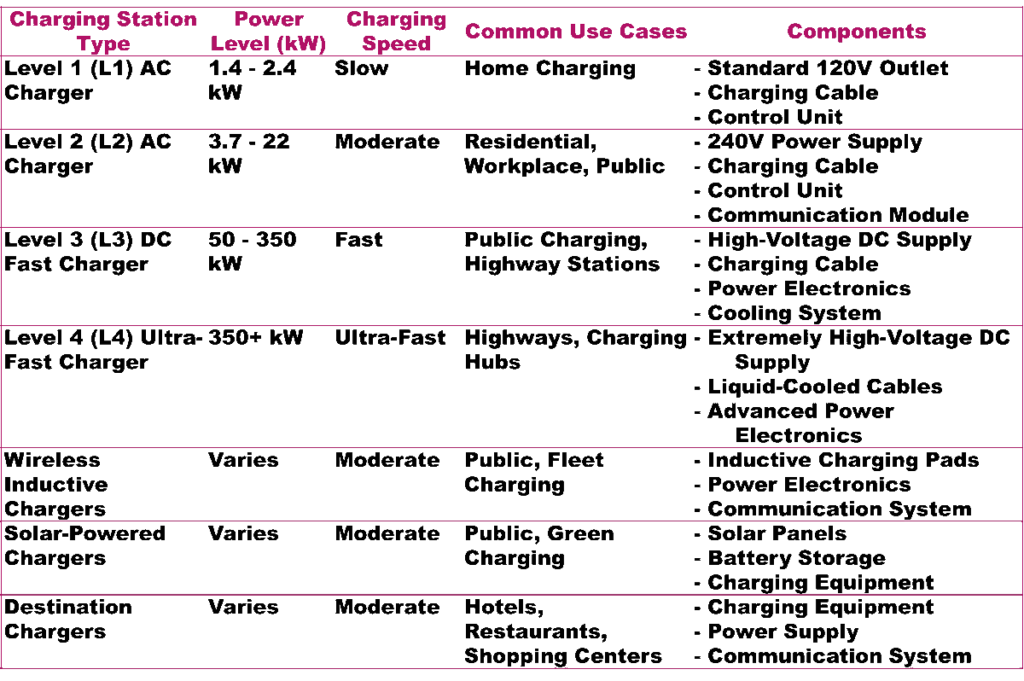
Electric vehicles can be charged using different methods, each with its own advantages and limitations. These methods include Level 1 charging (using standard home outlets), Level 2 charging (utilizing dedicated EV charging stations), and DC Fast Charging (high-speed public charging). Knowing the differences between these methods will help you choose the most suitable one for your needs.
Factors Affecting Battery Life and Range
The longevity of your EV’s battery and its overall range are influenced by several factors. These factors include temperature, driving habits, and the frequency of charging. By understanding how these variables affect your EV, you can take steps to maximize its efficiency and lifespan.
| Battery Chemistry | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Charge Time (minutes) | Cycle Life (cycles) | Safety | Cost |
| Lithium-Ion | High (150-250) | Moderate (30 mins – hours) | Moderate to High (500-1,000+) | Generally safe with management systems | Moderate to High |
| Solid-State | Promising (potentially higher) | Fast (15-30 projected) | High (projected > 1,000) | Expected to be safer | Currently high, expected to decrease |
| Nickel Metal Hydride (NiMH) | Variable (lower than Li-ion) | Moderate to Slow | Moderate (300-500) | Generally safe with variations | Moderate |
| Lithium Polymer (Li-Polymer) | Variable | Moderate to Fast | Moderate (300-500) | Generally safe with variations | Moderate |
| Lithium-Sulfur (Li-Sulfur) | Promising (potentially higher) | Moderate to Fast | Expected to be High | Ongoing research | Currently high, expected to decrease |
| Lead-Acid (Pb-Acid) | Low (30-40) | Slow (hours) | Moderate (300-500) | Requires careful handling | Low |
Key Points:
- Energy density is measured in watt-hours per kilogram (Wh/kg).
- Charge time represents typical charging speed.
- Cycle life refers to the number of charge-discharge cycles a battery can endure.
- Safety considerations vary, with some chemistries being inherently safer.
- Cost is relative and may change over time with advancements and production scale.
III. Level 1 Charging: Home Outlets
The Convenience and Considerations of Home Charging
Charging your electric vehicle at home is often the most convenient option. It allows you to start each day with a full battery, eliminating the need for frequent trips to public charging stations. However, there are important factors to consider when using home outlets for EV charging.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Home outlets, typically offering 120V or 240V options, provide several benefits, such as cost-effectiveness and accessibility. We’ll explore these advantages along with the drawbacks, such as slower charging speeds.
Charging Time and Cost Analysis
Understanding how long it takes to charge your EV using home outlets and the associated electricity costs is essential for budget-conscious EV owners. We’ll break down the numbers to help you plan your charging routine effectively.
Safety Considerations
Safety should always be a priority when charging your electric vehicle at home. We’ll provide guidelines and precautions to ensure a secure charging experience and prevent potential hazards.
IV. Level 2 Charging: Dedicated EV Charging Stations
Power and Convenience at Your Fingertips
Dedicated EV charging stations, also known as Level 2 charging stations, offer a faster and more efficient way to charge your electric vehicle compared to standard home outlets. In this section, we’ll explore the advantages of dedicated charging stations, the different types available, and important considerations.
Benefits of Dedicated EV Charging Stations
Dedicated charging stations bring several advantages to the table. They offer faster charging speeds, making it possible to replenish your EV’s battery in a shorter amount of time. This is particularly beneficial for those with longer commutes or frequent road trips.
Types of Level 2 Charging Stations (240V)
Level 2 charging stations come in various forms, including wall-mounted units, pedestal-mounted stations, and even portable options. We’ll discuss the differences between these types and help you choose the one that best suits your needs and budget.
Installation Costs and Rebates
While dedicated EV charging stations provide a faster charging experience, they do come with installation costs. We’ll provide insights into the installation process and discuss potential rebates and incentives that may help offset these expenses.
Network Connectivity and Smart Charging Features
Many Level 2 charging stations offer advanced features such as network connectivity and smart charging capabilities. We’ll explain how these features can enhance your charging experience and potentially save you money.
V. Public Charging Options
Charging on the Go: Your Guide to Public Charging Networks
As electric vehicles gain popularity, so does the infrastructure supporting them. Public charging networks have expanded rapidly, making it more convenient than ever to charge your EV while on the road. In this section, we’ll explore the world of public charging options.
Overview of Public Charging Networks
Public charging networks have grown to include numerous providers, each with its own set of charging stations. We’ll provide an overview of some of the prominent networks, giving you a sense of the coverage available in your region.
Finding Public Charging Stations Near You
Locating public charging stations has become easier thanks to various apps and websites dedicated to EV charging. We’ll introduce you to tools that help you find charging stations conveniently located along your routes.
Cost Comparison of Public vs. Home Charging
While public charging offers convenience, it often comes at a price. We’ll break down the cost comparison between public and home charging, helping you decide when it’s economical to use public stations and when it’s best to charge at home.
Tips for Efficient Use of Public Charging Stations
Efficiency matters when using public charging stations, especially during peak demand times. We’ll share tips on how to optimize your public charging experience, including when and where to charge for the quickest turnaround.
VI. Solar-Powered Charging
Charging with the Sun: A Sustainable Solution
Solar-powered charging systems offer an eco-friendly way to keep your electric vehicle’s battery topped up while reducing your reliance on traditional energy sources. In this section, we’ll explore the world of solar-powered charging for EVs.
Introduction to Solar-Powered Charging Systems
Solar-powered charging systems utilize sunlight to generate electricity, which is then used to charge your electric vehicle. We’ll explain the basics of how these systems work and their potential environmental benefits.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Solar-Powered Charging
Harnessing solar energy for EV charging comes with several advantages, including reduced electricity bills and lower carbon emissions. However, there are also some drawbacks to consider. We’ll provide a balanced overview to help you make an informed decision.
DIY vs. Professional Installation Options
You have the option to install solar panels and charging infrastructure yourself or hire professionals for the job. We’ll discuss the pros and cons of each approach, as well as considerations for both residential and commercial installations.
Cost Savings and Payback Period Analysis
One of the primary concerns for many prospective solar-powered EV owners is the cost. We’ll delve into the initial investment, potential savings on energy bills, and the payback period, helping you understand the financial implications.
VII. Energy Storage Systems
Powering the Future: Energy Storage for Electric Vehicles
Energy Storage Systems (ESS) are revolutionizing the way we charge and use electric vehicles. In this section, we’ll explore the role of ESS in enhancing the sustainability and efficiency of EV charging.
Overview of Energy Storage Systems (ESS)
ESS involves the use of advanced technologies to store electrical energy for later use. We’ll provide an overview of the concept and how it applies to electric vehicles.
Types of ESS Technologies
There are different technologies used in ESS, including lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries. We’ll explain the characteristics of each technology and how they impact EV charging and usage.
Using ESS for Backup Power During Outages
ESS can serve as a valuable backup power source during electrical outages, ensuring you stay mobile even when the grid is down. We’ll discuss the benefits and practicality of this feature.
Integration with Renewable Energy Sources
ESS can be integrated with renewable energy sources such as solar panels, further reducing your dependence on traditional grid electricity. We’ll explore the advantages of this synergy and how it contributes to sustainability.
VIII. Smart Charging Technologies
The Future of EV Charging: Smart and Efficient
Smart charging technologies are transforming the way we charge electric vehicles, making the process more efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly. In this section, we’ll dive into the world of smart charging.
Definition of Smart Charging and Its Benefits
Smart charging involves using advanced technology and data-driven strategies to optimize the charging process. We’ll define what smart charging is and discuss its numerous benefits, including reduced energy costs and improved grid stability.
Types of Smart Charging Technologies
There are various smart charging technologies available, including time-of-use charging and load management. We’ll explain each type, how they work, and their compatibility with different electric vehicle models.
Compatibility with Various EV Models
Smart charging technologies are designed to work with a wide range of electric vehicles, from cars to bikes and scooters. We’ll discuss the compatibility of these technologies with various EV models, ensuring that no matter what you drive, smart charging can benefit you.
Impact on Grid Stability and Demand Response
Smart charging not only benefits individual EV owners but also contributes to overall grid stability and supports demand response initiatives. We’ll explore how these technologies help balance electricity supply and demand.
IX. Government Incentives and Rebates
Maximizing Savings: Government Support for EV Charging
Governments at the federal, state, and local levels are incentivizing electric vehicle adoption by offering various financial benefits and rebates for EV charging infrastructure and electric vehicles themselves. In this section, we’ll explore the opportunities available to help you save on charging costs.
Federal Tax Credits for EV Charging Infrastructure
The U.S. federal government offers tax credits to offset the costs of installing EV charging infrastructure at homes and businesses. We’ll delve into the details of these credits and how to claim them.
State and Local Rebate Programs for Charging Equipment
Many states and local municipalities provide additional incentives, such as rebates, grants, or low-interest loans, to support the installation of EV charging equipment. We’ll discuss how to find and take advantage of these programs.
Incentives for Purchasing EVs and Plug-In Hybrids
Beyond charging infrastructure, governments also offer incentives for purchasing electric vehicles and plug-in hybrids. These incentives can significantly reduce the upfront cost of EV ownership. We’ll provide an overview of these incentives and how to qualify for them.
How to Find and Apply for Government Incentives
Navigating the world of government incentives and rebates can be daunting. We’ll offer guidance on how to find relevant programs in your area, how to apply for them, and the documentation required.
X. Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Keeping Your EV Running Smoothly: Maintenance and Solutions
Maintaining your electric vehicle is essential to ensure its longevity and trouble-free operation. In this section, we’ll cover everything you need to know about regular maintenance, common issues, warranties, and finding qualified technicians.
Regular Maintenance Tasks for EV Batteries and Charging Systems
Electric vehicle maintenance involves specific tasks to keep your battery and charging system in optimal condition. We’ll provide a checklist of routine maintenance items to help you maintain peak performance.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
Like any vehicle, electric cars and bikes may encounter common issues. We’ll identify these issues and offer troubleshooting tips to address them, saving you time and money on repairs.
Manufacturer Warranties and Support Resources
Understanding your vehicle’s warranty is crucial for minimizing repair costs. We’ll explain how manufacturer warranties work, what they cover, and how to access support resources in case of issues.
Finding Qualified Technicians for Repairs and Upkeep
When professional assistance is required, finding a qualified technician is essential. We’ll provide guidance on locating experienced technicians who specialize in electric vehicle repairs and maintenance.
XI. Summary and Final Thoughts
Charging Electric Vehicles on a Budget: Your Sustainable Journey
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored ten ways to charge electric vehicles on a budget, empowering you to make environmentally conscious and cost-effective choices. Let’s summarize the key takeaways and offer some final thoughts.
Recap of the 10 Ways to Charge Electric Bikes and Autos on a Budget
- Level 1 Charging: Using standard home outlets for convenience.
- Level 2 Charging: Leveraging dedicated EV charging stations for faster charging.
- Public Charging Options: Utilizing public charging networks for on-the-go replenishment.
- Solar-Powered Charging: Harnessing solar energy for eco-friendly charging.
- Energy Storage Systems (ESS): Integrating ESS technology for grid stability and backup power.
- Smart Charging Technologies: Optimizing charging with data-driven strategies.
- Government Incentives and Rebates: Taking advantage of financial support for EV infrastructure and purchases.
- Regular Maintenance: Keeping your EV in top shape with routine tasks.
- Common Issue Resolution: Addressing common problems with troubleshooting tips.
- Professional Support: Finding qualified technicians when professional help is needed.
Encouragement to Adopt Sustainable Transportation Solutions
By choosing electric vehicles and sustainable charging methods, you’re contributing to a greener and cleaner future. Your actions can inspire others to follow suit and reduce their environmental impact.
Call to Action
We encourage you to explore affordable charging options, take advantage of government incentives, and prioritize sustainability in your transportation choices. Together, we can create a more sustainable and eco-friendly world.
Thank you for joining us on this journey to discover budget-friendly ways to charge electric vehicles. If you have any more questions or need further assistance, feel free to reach out.
FAQs
Now, let’s address the frequently asked questions (FAQs) related to electric vehicle charging:
- What is the cheapest way to charge my electric car?
- The cheapest method depends on various factors, including your location, driving habits, and access to charging infrastructure. Level 1 charging at home is typically the most cost-effective, but public charging or solar-powered options may also be economical in certain situations.
- Can I charge my electric bike from a regular wall outlet?
- Yes, you can charge most electric bikes from a standard 120V or 240V wall outlet, similar to electric cars. However, charging times may vary based on the bike’s battery capacity and the charging voltage.
- Are there any grants available for installing an EV charging station at home?
- Yes, there are often grants and incentives at the state and local levels to support the installation of home EV charging stations. Check with your local authorities or utility companies for available programs.
- Is it worth investing in a solar-powered charging system for my electric vehicle?
- The worth of a solar-powered charging system depends on your location, sun exposure, and electricity rates. It can offer significant long-term savings and environmental benefits if these conditions align with your situation.
- Can I use a portable generator to charge my electric car during a power outage?
- While it’s possible to use a portable generator for emergency charging, it’s not the most efficient or eco-friendly option. Dedicated backup power solutions or energy storage systems (ESS) may be more reliable during outages.
Conclusion
In conclusion, charging electric vehicles on a budget is not only feasible but also a crucial step towards a more sustainable future. By exploring the various charging methods and incentives available, you can reduce costs while contributing to a cleaner environment.
| Cost Comparison (Per Mile) | Petrol Car | Diesel Car | Conventional Car (Gasoline) | Electric Vehicle (EV) |
| Fuel Type | Petrol (INR per liter) | Diesel (INR per liter) | Gasoline (USD per gallon) | Electricity (USD per kWh) |
| Average Fuel Price | ₹100 per liter (approximate) | ₹90 per liter (approximate) | $3.00 per gallon | $0.12 per kWh |
| Fuel Efficiency | 15 kilometers per liter (approximate) | 20 kilometers per liter (approximate) | 25 miles per gallon (mpg) | 3.5 miles per kWh |
| Cost per Mile | ₹6.67 per kilometer (approximate) | ₹4.50 per kilometer (approximate) | $0.12 per mile | $0.034 per mile |
Reading resources
- Tesla’s Electric Vehicle Charging Network
URL: https://www.tesla.com/supercharger
Why: Tesla is a leading company in electric vehicles and charging infrastructure. Linking to their official Supercharger network page demonstrates your content’s connection to a reputable source in the EV industry.
- IEEE Spectrum – Electric Vehicles
URL: https://spectrum.ieee.org/electric-vehicles
Why: IEEE Spectrum is a respected publication in the field of technology and engineering. This section specifically covers electric vehicles, making it a reliable source for technical insights and updates.
- The Official Electric Vehicle Association
Why: Associations often provide valuable information and industry standards.
- EV Charging Infrastructure Trends – Statista
Why: Statista is known for its reliable statistics and data. This page provides statistics on the global EV charging infrastructure, adding factual support to your content.
- How Electric Cars Work – Explain that Stuff
URL: https://www.explainthatstuff.com/electriccars.html
Why: This page explains the fundamental workings of electric cars, making it an educational resource. Linking to it complements your interest in teaching and developing courses.