- Introduction to Prototyping
- The Role of Prototyping in Bridging Ideas with Reality
- Different Types of Prototypes and Their Purposes
- The Stages of Process Design in Prototyping
- 5 Ways Prototyping Empowers Design Success
- Conclusion: Embracing Prototyping for Innovation
- FAQ: The Power of Prototyping
- Further Reading on Prototyping
Introduction to Prototyping
Important Points:
- प्रोटोटाइपिंग की महत्वता – Importance of Prototyping: Essential for innovation and design.
- अभिनव समाधानों के लिए प्रोटोटाइपिंग – Prototyping for Innovative Solutions: Turns ideas into tangible outcomes.
- त्वरित प्रतिक्रिया प्राप्त करना – Obtaining Rapid Feedback: Facilitates quick improvements.
- उत्पाद विकास की गति – Speeding Up Product Development: Accelerates the development cycle.
- उपयोगकर्ता-केंद्रित डिज़ाइन में योगदान – Contributing to User-Centered Design: Enhances user experience.
Explanation:
- Prototyping is a critical phase in the innovation and design process, allowing teams to transform ideas into tangible, testable products. It enables the early detection of potential issues, encouraging iterative improvements based on rapid feedback from real users or stakeholders. This approach not only speeds up the product development cycle but also ensures the final product is aligned with user needs, thus contributing significantly to user-centered design.
The Role of Prototyping in Bridging Ideas with Reality
Important Points:
- वास्तविक दुनिया में प्रोटोटाइपिंग के उदाहरण – Examples of Prototyping in the Real World: Showcasing successful case studies.
- उत्पाद विकास पर प्रभाव – Impact on Product Development: How prototyping enhances product quality.
- समस्या-समाधान की क्षमता – Problem-Solving Capacity: Prototyping as a tool for addressing challenges.
- नवाचार में तेजी – Accelerating Innovation: Speeding up the innovation process.
- असफलताओं से सीखने का महत्व – The Importance of Learning from Failures: Embracing mistakes as learning opportunities.
Explanation:
- Real-world examples like the development of the Dyson vacuum cleaner, which underwent thousands of prototypes, illustrate the impact of prototyping on product development. This process not only helps in resolving specific design challenges but also accelerates innovation by allowing designers to experiment freely and learn from failures. Such an approach is instrumental in enhancing product quality and user satisfaction.
Different Types of Prototypes and Their Purposes
Important Points:
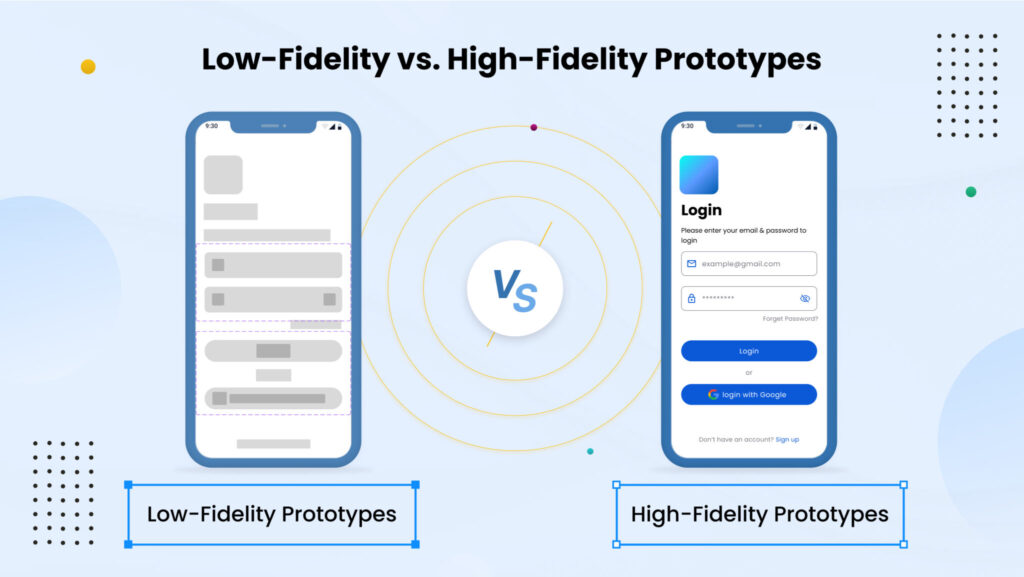
- प्रोटोटाइप के प्रकार – Types of Prototypes: Low-fidelity vs. high-fidelity.
- प्रत्येक प्रकार का उद्देश्य – Purpose of Each Type: Validation, testing, and refinement.
- केस स्टडी – Case Studies: Examples of different prototypes in action.
- विचारों की व्यवहार्यता – Testing Idea Feasibility: Using prototypes for feasibility studies.
- उपयोगकर्ता प्रतिक्रिया का महत्व – Importance of User Feedback: Guiding design decisions.
Explanation:
- Prototypes can range from low-fidelity (simple sketches or paper models) to high-fidelity (working models). Each serves a different purpose:
- Low-fidelity prototypes are quick and easy to produce, ideal for initial concept validation and gathering early user feedback.
- High-fidelity prototypes are closer to the final product, used for detailed testing and refinement.
- Case studies, such as the iterative development of a mobile app interface, demonstrate how different prototypes are employed at various stages of the development process to test functionality, usability, and overall user experience. For instance, a low-fidelity prototype might be used to validate the overall flow of the app, while a high-fidelity prototype could be employed to test specific interactions and the integration with backend systems.
- Testing idea feasibility with prototypes allows teams to assess whether their concepts can be turned into viable products. This might involve technical feasibility, market feasibility, or both, depending on the nature of the project.
- User feedback is crucial at every stage of prototyping. It guides the design decisions, ensuring that the final product meets the needs and expectations of its intended users. For example, user feedback on a digital wallet app’s prototype might highlight the need for simpler navigation, prompting designers to refine the interface in subsequent iterations.
| Feature | Low-Fidelity Prototypes | High-Fidelity Prototypes |
| Definition | Basic models that focus on the broad concept of a product, often lacking detailed functionality. | Detailed and interactive models that closely mimic the final product in terms of design and functionality. |
| Purpose | To quickly explore and communicate design concepts, facilitate early discussions, and identify major flaws or changes. | To test specific interactions, technical feasibility, and overall user experience with a design that’s close to the final product. |
| Materials Used | Paper, cardboards, sketches, and basic digital mockups. | Advanced software for digital prototypes, materials close to the final product for physical prototypes. |
| Time to Create | Generally quick to produce, ranging from a few minutes to a few hours. | Can take several days to weeks, depending on complexity and detail. |
| Cost | Low, due to the simplicity and use of readily available materials. | Higher, due to the need for specialized software or materials. |
| Fidelity | Low fidelity, focusing more on concepts than on detailed execution. | High fidelity, with a focus on detailed execution and interactivity. |
| User Testing | Used for initial concept validation, understanding user needs, and gathering feedback on the general direction. | Used for detailed usability testing, understanding user interactions, and gathering specific feedback on features and design. |
| Iteration Speed | Fast, allowing for rapid changes based on feedback. | Slower, as changes require more effort and resources. |
| Typical Use Cases | Early stages of design to explore ideas and concepts. | Later stages of design for refining and validating detailed interactions and functionality. |
Examples of Low-Fidelity Prototyping
Low-fidelity prototypes are basic representations of products that help in the early stages of design. They are quick to create, inexpensive, and effective for exploring concepts and facilitating early discussions on design directions. Here are some common examples:
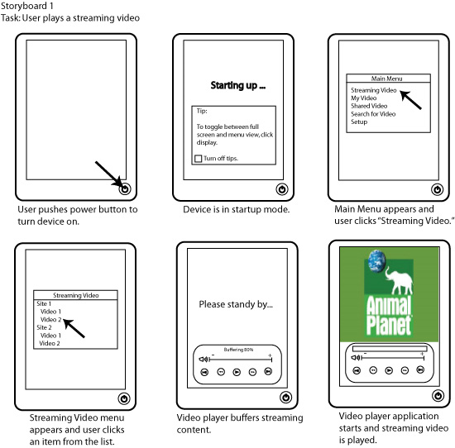
- Storyboards: Storyboards are visual narratives in a sequence of panels. They illustrate how users interact with a product over time, providing a clear picture of the user journey. This method is particularly useful for outlining scenarios and envisioning how users will navigate through a system.
- Sketching: Perhaps the simplest form of prototyping, sketching allows designers to quickly draw ideas on paper. It’s an effective way to brainstorm and share concepts with team members or stakeholders without investing time in detailed designs.
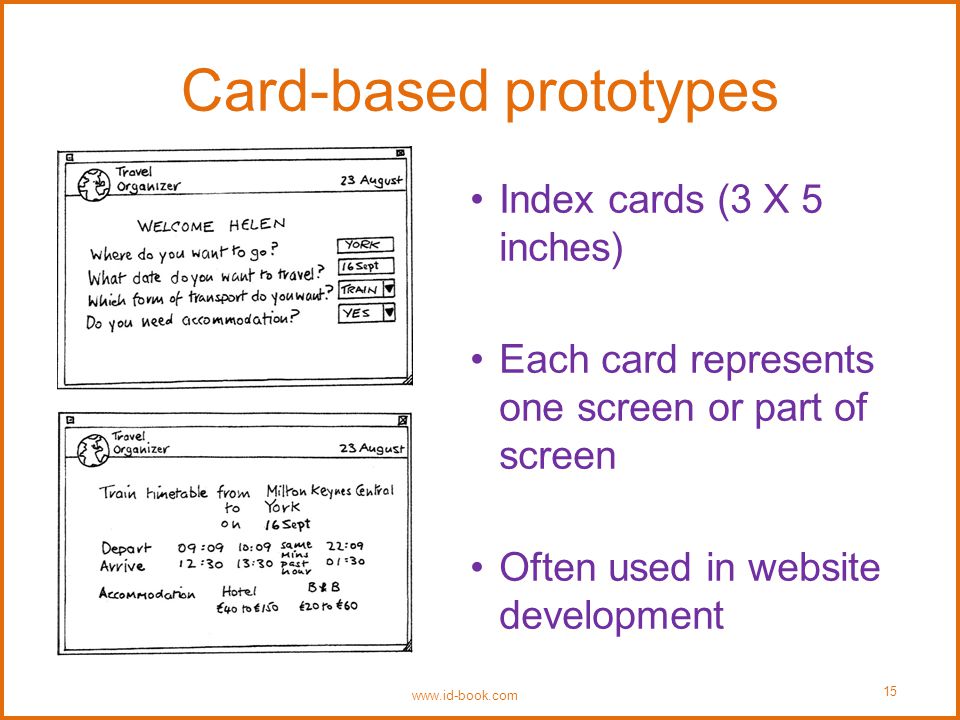
- Index Cards: Using index cards to represent different parts of a user interface can be a powerful tool for organizing and rearranging components. This method is especially handy for planning the layout of web pages or app screens, allowing for easy adjustments and iterations.
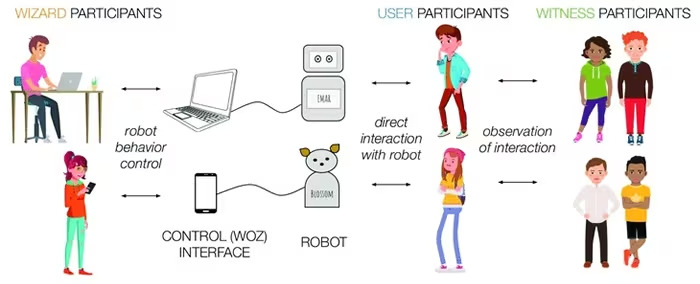
- ‘Wizard of Oz’ Prototyping: This technique involves simulating the functionality of a digital system through human intervention without the user’s knowledge. It’s used to test concepts where the technology might not yet exist or be too costly to implement for testing purposes. This approach helps validate user interactions and gather feedback on the concept.
Examples of High-Fidelity Prototyping
High-fidelity prototypes are more detailed and closely resemble the final product, both in appearance and, often, in functionality. They are useful for detailed usability testing and for demonstrating concepts to stakeholders. Here are some aspects and tools associated with high-fidelity prototyping:
- Choice of Materials and Methods: High-fidelity prototypes use materials and methods that are similar or identical to those in the final product. This approach ensures that the prototype is as close to the end product as possible, allowing for more accurate testing and feedback.
- Appearance Like the Final System: While high-fidelity prototypes may focus on appearance, including the user interface and visuals, they might not fully replicate the functionality of the final system. They are designed to look and feel like the end product, helping stakeholders and users to visualize the final outcome.
- Common Development Environments: Tools such as Macromedia Director, Visual Basic, Smalltalk, and various web development tools are often used to create high-fidelity prototypes. These environments allow designers and developers to build interactive and functional prototypes that closely mimic the final product.
- Misled User Expectations: One potential downside of high-fidelity prototyping is that it can lead to misled user expectations. Users might believe they are interacting with a fully functional system, not realizing it’s a prototype. This misconception can affect the feedback and perceptions of the prototype’s performance.
Both low-fidelity and high-fidelity prototyping have their place in the design process, serving different purposes at various stages of development. Choosing the right approach depends on the goals of the prototype, the stage of development, and the resources available.
The Stages of Process Design in Prototyping
Important Points:
- प्रोटोटाइपिंग के चरण – Stages of Prototyping: Conceptualization, development, testing.
- चरण-दर-चरण विवरण – Step-by-Step Description: Detailed walkthrough of each stage.
- उदाहरण – Examples: Real-life examples of the stages in action.
- टीम की भूमिका – Role of the Team: Collaboration and roles in the prototyping process.
- संशोधन और सुधार – Revision and Refinement: Importance of iterative design.
Explanation:
- The prototyping process generally involves several key stages:
- Conceptualization: Identifying the problem and brainstorming potential solutions.
- Development: Creating the initial prototype based on the chosen concept.
- Testing: Evaluating the prototype with real users or stakeholders to gather feedback.
- Revision and Refinement: Making necessary changes based on feedback and testing again.
- A step-by-step description provides a clear framework for teams to follow. For example, during the conceptualization stage, a team might use mind maps or storyboards to outline the user journey for a new fitness app.
- Real-life examples include the development of a smartwatch prototype, where the team went through multiple iterations, starting from a basic design to test the concept, followed by more sophisticated versions to refine the user interface and functionality.
- The role of the team is crucial in this process. Effective collaboration between designers, engineers, and product managers ensures a cohesive approach to prototyping and problem-solving.
- Iterative design underscores the importance of revising and refining prototypes. Each iteration brings the product closer to its final form, incorporating lessons learned from previous rounds of feedback. This approach is epitomized by the development of consumer electronics, where products undergo numerous refinements before reaching the market.
5 Ways Prototyping Empowers Design Success
- विचारों को त्वरित रूप से परखना (Rapid Testing of Ideas): प्रोटोटाइपिंग से डिज़ाइन टीमें त्वरित और कुशलतापूर्वक विचारों की परख कर सकती हैं, जिससे विकास प्रक्रिया में गति आती है।
- उपयोगकर्ता प्रतिक्रिया के माध्यम से सुधार (Improvement Through User Feedback): प्रोटोटाइप्स का परीक्षण वास्तविक उपयोगकर्ताओं के साथ किया जाता है, जो मूल्यवान प्रतिक्रिया प्रदान करते हैं और डिज़ाइन में सुधार करने में मदद करते हैं।
- नवाचार में तेजी (Accelerating Innovation): प्रोटोटाइपिंग नवीन विचारों को जल्दी से परीक्षण और विकसित करने में सहायता करता है, जिसस से विकास की प्रक्रिया में नवीनता लाने में सहायता मिलती है।
- उत्पाद विकास में तेजी लाना (Speeding Up Product Development): जटिल उत्पाद विकास प्रक्रियाओं में समय की बचत होती है, जिससे परियोजनाओं को तेजी से बाजार में पहुंचाया जा सकता है।
- सीखने और सुधार के लिए असफलताओं को अपनाना (Embracing Failures for Learning and Improvement): प्रोटोटाइपिंग असफलताओं को एक सीखने के अवसर के रूप में अपनाने की संस्कृति को बढ़ावा देता है, जो डिज़ाइन और नवाचार में सुधार की ओर ले जाता है।
- Rapid Testing of Ideas: Prototyping allows design teams to quickly and efficiently test ideas, speeding up the development process.
- Improvement Through User Feedback: Prototypes are tested with actual users, providing valuable feedback that helps in refining the design.
- Accelerating Innovation: Prototyping assists in quickly developing and testing innovative ideas, contributing to the acceleration of the innovation process.
- Speeding Up Product Development: Saves time in complex product development processes, allowing projects to be launched more quickly into the market.
- Embracing Failures for Learning and Improvement: Prototyping promotes a culture of embracing failures as opportunities for learning, leading to improvements in design and innovation.
Conclusion: Embracing Prototyping for Innovation
Importance of prototyping
प्रोटोटाइपिंग केवल उत्पाद विकास प्रक्रिया का एक चरण नहीं है; यह एक दर्शन है जो प्रयोग, सीखने और पुनरावृत्ति को अपनाता है। विभिन्न प्रकार के प्रोटोटाइप्स को प्रक्रिया डिज़ाइन के विभिन्न चरणों में प्रभावी रूप से नियोजित करके, डिज़ाइन टीमें अपने उत्पादों की गुणवत्ता और उपयोगिता को काफी बढ़ा सकती हैं। इस लेख में उल्लिखित वास्तविक दुनिया के उदाहरण और केस स्टडीज प्रोटोटाइपिंग की परिवर्तनकारी शक्ति को दर्शाते हैं, जो विचारों को वास्तविकता में बदलने, नवाचार को तेज करने और अंततः उपयोगकर्ता की अपेक्षाओं को पूरा करने वाले समाधान देने में मदद करता है। प्रोटोटाइपिंग आधुनिक उत्पाद विकास का एक महत्वपूर्ण स्तंभ बना हुआ है, जो रचनाकारों को संभावनाओं की खोज करने और दूरदर्शी अवधारणाओं को ठोस वास्तविकताओं में बदलने की शक्ति प्रदान करता है।
प्रोटोटाइपिंग प्रक्रिया डिज़ाइन के चरणों को संरचित तरीके से अपनाकर और उपयोगकर्ता प्रतिक्रिया को मूल्यवान मानकर, संगठन नवाचार की एक संस्कृति को बढ़ावा दे सकते हैं जो लगातार सुधार और परिष्कार की तलाश करती है। आज की तेज़ी से बदलती दुनिया में, जहाँ उपयोगकर्ता की ज़रूरतों के प्रति अनुकूलनशीलता और प्रतिक्रियाशीलता किसी भी संगठन की प्रतिस्पर्धी बढ़त बनाए रखने की कुंजी हैं, प्रोटोटाइपिंग केवल विकास का एक उपकरण नहीं बल्कि प्रभावशाली उपयोगकर्ता-केंद्रित समाधान बनाने के लिए प्रतिबद्ध किसी भी संगठन के लिए एक रणनीतिक संपत्ति है।
Importance of prototyping
Prototyping is not just a step in the product development process; it’s a philosophy that embraces experimentation, learning, and iteration. By effectively employing different types of prototypes at various stages of the process design, teams can significantly enhance the quality and usability of their products. The real-world examples and case studies mentioned throughout this article illustrate the transformative power of prototyping in bridging ideas with reality, accelerating innovation, and ultimately delivering solutions that meet and exceed user expectations. Prototyping remains a cornerstone of modern product development, empowering creators to explore the realms of possibility and turn visionary concepts into tangible realities.
By adopting a structured approach to prototyping, as outlined in the stages of process design, and valuing user feedback, organizations can foster a culture of innovation that continuously seeks to improve and refine. This mindset is essential in today’s fast-paced world, where adaptability and responsiveness to user needs are key to maintaining a competitive edge. Prototyping, therefore, is not just a tool for development but a strategic asset for any organization committed to creating impactful, user-centered solutions.
FAQ: The Power of Prototyping
1. What is prototyping and why is it important?
- Prototyping is a phase in the innovation and design process that allows teams to transform ideas into tangible, testable products. It’s crucial for early detection of potential issues, facilitating quick improvements based on real user feedback, and ensuring the final product aligns with user needs.
2. How does prototyping contribute to product development?
- Prototyping accelerates the product development cycle by enabling designers to experiment, test, and refine ideas quickly. It helps in resolving design challenges, enhancing product quality, and ensuring user satisfaction.
3. What are some real-world examples of successful prototyping?
- The development of the Dyson vacuum cleaner, which underwent thousands of prototypes, is a prime example. It illustrates how prototyping can significantly impact product development and innovation.
4. What are the different types of prototypes?
- Prototypes can range from low-fidelity (simple sketches or paper models) for initial concept validation to high-fidelity (working models) for detailed testing and refinement.
5. How does user feedback play a role in prototyping?
- User feedback is crucial at every stage of prototyping. It guides design decisions and ensures that the final product meets the needs and expectations of its intended users.
6. Can you provide an example of the stages of prototyping?
- The prototyping process typically involves conceptualization (identifying the problem and brainstorming solutions), development (creating the initial prototype), testing (evaluating the prototype with users), and revision/refinement (making changes based on feedback).
7. How does prototyping foster innovation?
- Prototyping fosters innovation by allowing designers and engineers to explore, experiment, and learn from failures. This iterative process encourages creativity and leads to the development of groundbreaking products.
8. What is the significance of learning from failures in prototyping?
- Learning from failures is vital in prototyping as it provides valuable insights that can be used to improve future iterations. Embracing mistakes as learning opportunities is essential for continuous innovation and refinement.
9. How can organizations adopt a prototyping mindset?
- Organizations can foster a culture of innovation by embracing prototyping as a philosophy, encouraging experimentation, and valuing iterative design and user feedback.
10. What are some case studies of prototyping in action?
- Besides the Dyson vacuum cleaner, other case studies include the iterative development of mobile app interfaces, where different prototypes are employed to test functionality, usability, and overall user experience.
This FAQ section provides a concise overview of prototyping, addressing common questions and offering insights into its benefits, processes, and impact on product development and innovation.
Further Reading on Prototyping
For those interested in diving deeper into the concept of prototyping and its application in design and development, the following resources offer valuable insights, guidance, and case studies. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a curious newcomer, these readings can enhance your understanding and skills in prototyping.
General Prototyping Resources:
- Interaction Design Foundation: What is Prototyping?
A comprehensive guide that delves into the essence of prototyping, explaining its various types and the pivotal role it plays in the design process. Perfect for those seeking a thorough understanding of prototyping principles.
Read more - Usability.gov: Prototyping
This resource provided by the U.S. government offers a unique user-centered perspective on prototyping. It includes practical advice on creating effective paper prototypes and insights into how prototyping fits into the broader scope of user experience design.
Explore further - Simplilearn: Prototyping In Design Thinking
An enlightening article that explores the critical role of prototyping within the design thinking process. It highlights how prototyping contributes to refining design solutions and enhancing design precision, making it a must-read for practitioners of design thinking.
Discover more
Specific Types of Prototyping:
- Low-Fidelity vs. High-Fidelity Prototypes
This insightful article examines the distinctions between low-fidelity and high-fidelity prototypes, offering guidance on when and how to use each type effectively in the design process. A useful read for those looking to apply the most appropriate prototyping techniques to their projects.
Learn about the differences
These resources provide a solid foundation for understanding and applying prototyping in various stages of product development and design. By exploring these materials, you can gain deeper insights into how prototyping can be leveraged to bring innovative ideas to life and ensure that final products meet the needs and expectations of users.